Measuring Current in Parallel Circuits
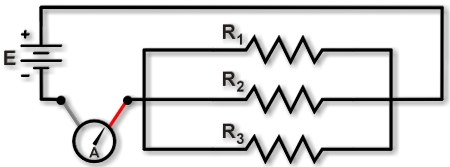 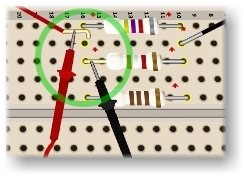 Figure 1. Measuring current for whole circuit. |
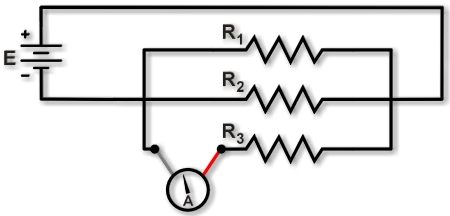 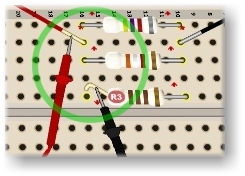 Figure 2. Measuring current through resistor R3. |
To measure current, you must insert the ammeter into the circuit to intercept the electric charge flowing in the wires. That means you must "break the circuit" by lifting a lead, and then complete the circuit using the probes of the ammeter.
To measure a circuit's total current, lift a lead connected to the battery (or power source) and insert the ammeter, as shown in Figure 1. On a breadboard, this requires lifting the lead that provides power to the parallel resistors. The ammeter then measures the sum of the current through all the parallel resistors.
To measure the current through just one resistor, lift one resistor's lead and insert the ammeter, as shown in Figure 2. On a breadboard, this requires lifting the lead of one resistor and connecting the ammeter probes between the lifted lead and the power source. The ammeter then measures the current through a single resistor.
Look closely to note the subtle differences between Figure 1 and Figure 2.
